Romosozumab (로모소주맙, 이베니티주프리필드시린지) [골다공증 치료제]
https://blog.naver.com/sjloveu2/222042011558

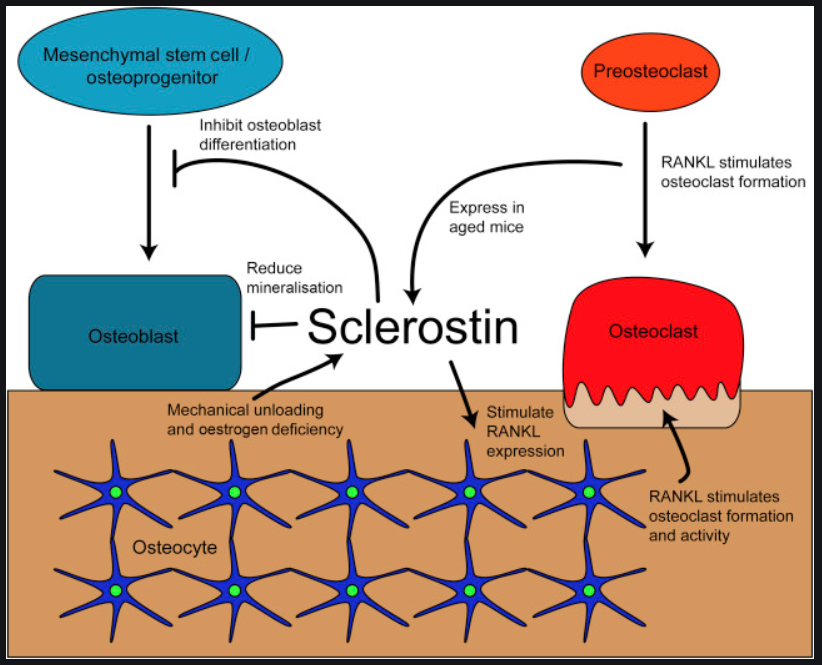
Sclerostin (스클레로스틴)은 osteocytes에서 생성되고 bone formation을 억제합니다. Romosozumab (로모소주맙)은 monoclonal anti-sclerostin antibody입니다.
|
Osteocytes are the predominant cellular source of the Wnt antagonist sclerostin, a limiting factor for osteoblast generation and bone mass accrual that mediates the homeostatic adaptation of bone to mechanical loading. Sclerostin is the product of the SOST gene and a negative regulator of Wnt signaling. It binds to both LRP5 and LRP6 and prevents activation of the Wnt receptor complex. This results in inhibition of bone formation. In addition to sclerostin, the DKK family members, particularly DKK-1 (Dickkopf-1), inhibit the Wnt pathway by binding to the LPR5/6 receptor. Wnt signaling can also be blocked by other proteins, such as soluble frizzled-related protein, that bind to Wnt ligands. |
한편, 스클레로스틴은 Wnt signal pathway에서 나오는데
스클레로스틴은 LRP-5/6 receptors와 결합하여 bone formartion을 억제시키는 역할을 하는데
로모소주맙은 이 스클레르스틴과 결합하여 스클레로스틴의 bone formation억제 효과를 막습니다.

Role of the Wnt signaling pathway


|
Wnt signaling pathway — The Wnt signaling pathway is another critical regulator of skeletal development and mass, working in part through the stimulation of Runx2 gene expression. Activation of the canonical Wnt signaling involves the formation of a complex between Wnt proteins, frizzled and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) or LRP6 receptors. This complex in turn leads to phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta, inhibition of beta-catenin degradation, and subsequent accumulation of beta-catenin in the nucleus. Nuclear beta-catenin binds the Tcf/Lef family of transcription factors and induces target gene expression |
REF. UpToDate 2020.07.26
'내분비내과 > 골다공증' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 비스포스포네이트, 작용기전, Bisphosphonate, mechanism of action (0) | 2020.07.28 |
|---|---|
| PTH의 만성 노출은 bone resoption을 초래하지만 recombinant human PTH 간헐적 투여는 bone formation을 자극합니다. (0) | 2020.07.27 |
| Romosozumab (로모소주맙, 이베니티주프리필드시린지) [골다공증 치료제] (0) | 2020.07.26 |
| 골밀도 측정 방법, Interpretation of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) in evaluating osteoporosis (0) | 2020.07.11 |
| 폐경 전 여성과 50세 이하의 남성의 골밀도 해석 (0) | 2020.07.05 |



