What's New
Surgical versus medical therapy for heartburn refractory to proton-pump inhibitors (October 2019)
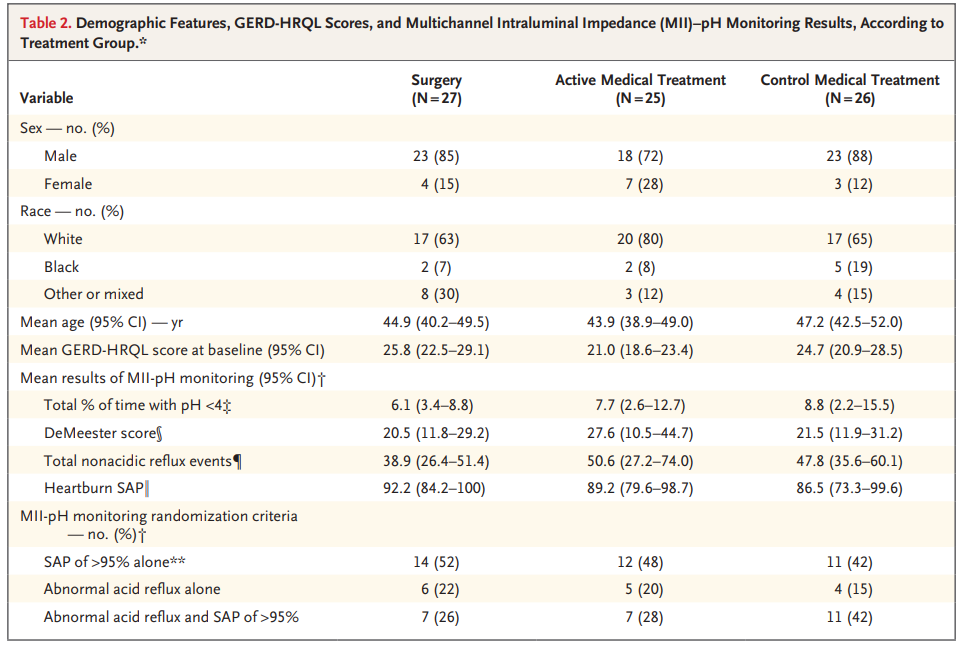
The optimal approach to heartburn refractory to proton-pump inhibitors (PPI) is debated. In a randomized trial, patients with heartburn refractory to a two-week course of double-dose omeprazole underwent endoscopy, esophageal biopsy, esophageal manometry, and multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring while on PPI therapy. One-fifth had objective evidence that their symptoms were related to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and were randomly assigned to receive laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication, active medical management (omeprazole+baclofen±desipramine), or control medical management (omeprazole+placebo). At one year, the proportion of patients in the surgery, active medical, and control medical management groups that achieved ≥50 percent improvement in a GERD quality of life score was 67, 28, and 12 percent, respectively. These results support the efficacy of antireflux surgery, but also underscore the importance of careful patient selection, as 79 percent of patients referred for PPI-refractory heartburn lacked objective evidence of GERD.

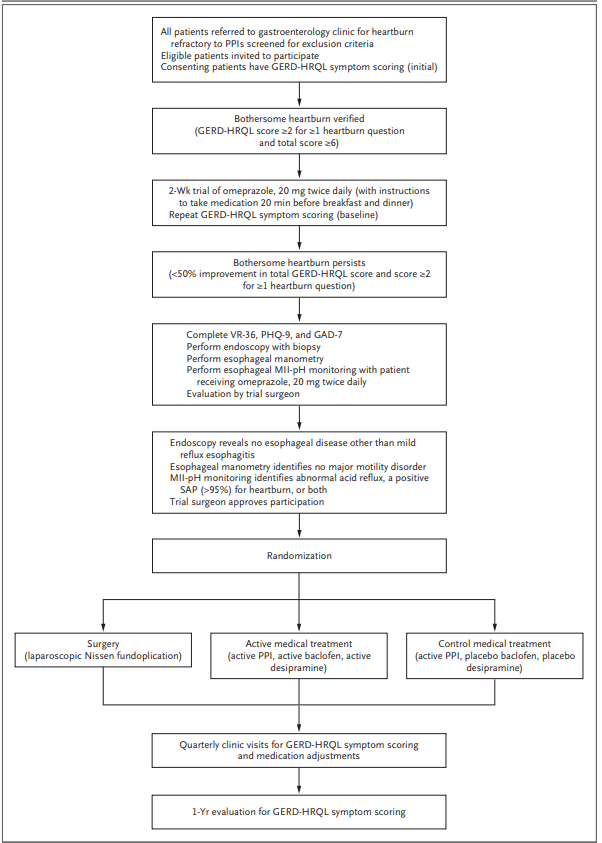
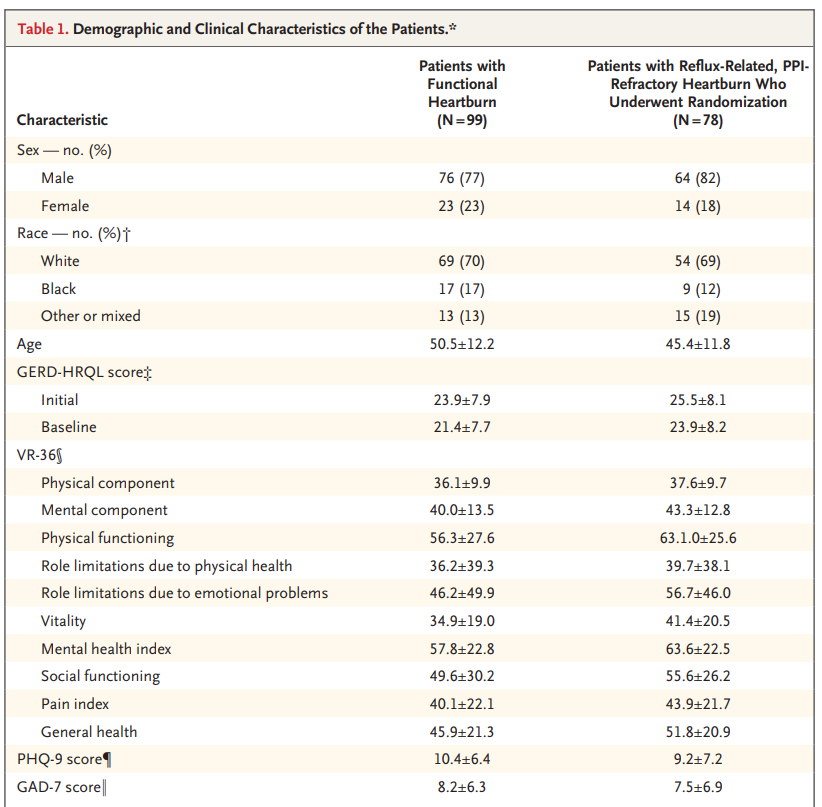





REF. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(16):1513.
UpToDate 2020.03.25
'소화기내과(위장관) > 식도' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 말로리-바이스 증후군, 내시경 소견, Most tears may be missed if endoscopy is delayed (0) | 2020.07.16 |
|---|---|
| 칸디다 식도염, 치료제, Esophageal candidiasis, systemic antifungal therapy (0) | 2020.03.26 |
| 말로리-바이스 증후군, MALLORY-WEISS TEARS (0) | 2020.03.25 |
| 식도이완불능증의 치료 선택, Choice of treatment, achalasia (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| 연하곤란의 증상에 근거한 감별 진단, Symptom-based differential diagnosis of dysphagia (0) | 2020.02.16 |



