

|
PV should be suspected in any patient with an increased red blood cell mass or increased hemoglobin/hematocrit and an arterial oxygen saturation >92 percent. To be considered for the diagnosis, men should have a hemoglobin level of at least 16.5 g/dL or a hematocrit level of ≥49 percent, and women should have a hemoglobin level of at least 16 g/dL or a hematocrit level of ≥48 percent. PV should also be suspected in patients with the Budd-Chiari syndrome and portal, splenic, or mesenteric vein thrombosis, particularly women under the age of 45. In this setting, the ensuing portal hypertension and hypersplenism may mask the increase in blood cell counts. Additional evidence suggesting the diagnosis of PV includes the following: ■ Splenomegaly ■ Thrombocytosis and/or leukocytosis ■ Thrombotic complications ■ Erythromelalgia or aquagenic pruritus ■ Microvascular symptoms (eg, headaches, paresthesias) |
2018년 혈액검사

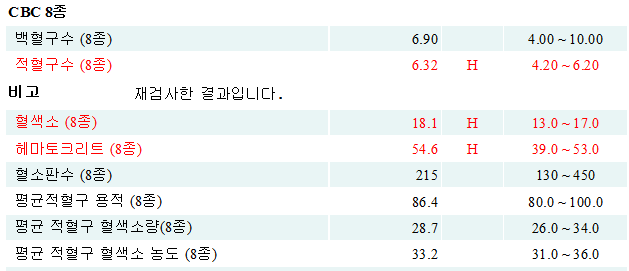
2021년 혈액검사
'봉직, 개원 > 봉직, 개원' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [외래진료14] 철결핍성빈혈에서 백혈구 감소증 (0) | 2021.01.19 |
|---|---|
| [외래진료13] 요소호기검사 전 주의해야 할 약물 복용 (0) | 2021.01.15 |
| [외래 진료10] 불완전 우각차단 (0) | 2021.01.10 |
| [외래 진료8] 아토르바스타틴과 설사 (0) | 2021.01.09 |
| [외래 진료6] 천식의 급성 악화시에는 흡입 스테로이드 (0) | 2021.01.09 |



