What's New
Timing of blood cultures in patients with sepsis (October 2019)
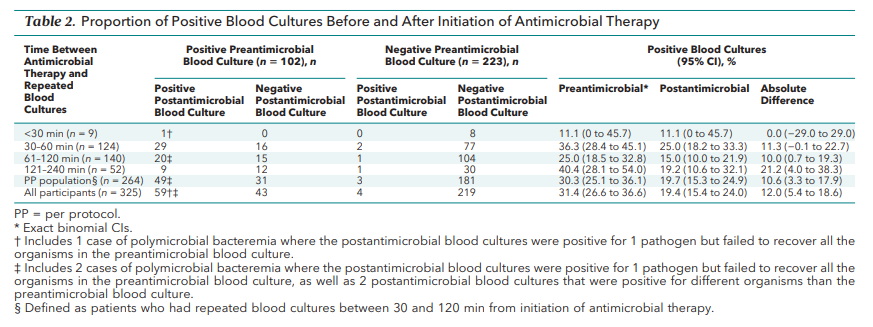
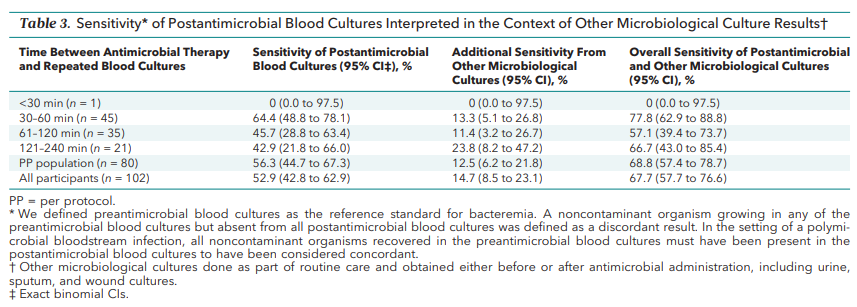
Data describing the impact of antimicrobial administration on the sensitivity of blood cultures are lacking. A recent study of 325 adults presenting to the emergency department with sepsis reported that pre-antimicrobial blood cultures were more likely to identify a pathogen compared with blood cultures drawn from the same patient one to two hours after antibiotics were given (31 versus 19 percent). When pre-antimicrobial cultures were considered the reference gold standard, the sensitivity of post-antimicrobial blood cultures was only 53 percent. In keeping with this study, we recommend that aggressive efforts be targeted at obtaining blood cultures before the timely administration of antimicrobial therapy.
Peripheral blood cultures (aerobic and anaerobic cultures from at least two different sites), urinalysis, and microbiologic cultures from suspected sources (eg, sputum, urine, intravascular catheter, wound or surgical site, body fluids) from readily accessible sites. Drawing blood for cultures through an indwelling or central intravascular catheter should be avoided whenever possible, since ports are frequently colonized with skin flora, thereby increasing the likelihood of a false-positive blood culture. If blood cultures are drawn from an intravenous line, a second specimen should be drawn from a peripheral venipuncture site.
The importance of early blood cultures was best illustrated in a multicenter randomized trial of 325 patients with a presumed or confirmed source of infection and hypotension, or elevated lactate >4 mmol/L. All patients had two sets of blood cultures drawn from two separate sites before antimicrobial administration and a second set of blood cultures were obtained from zero to four hours after antimicrobial administration. Pre-antimicrobial cultures were positive in 31.4 percent compared with 19.4 percent post-antimicrobial administration. When pre-antimicrobial cultures were considered the reference gold standard, the sensitivity of post-antimicrobial blood cultures was 53 percent. When other cultures were included with post-antimicrobial blood cultures, pathogens were identified in approximately two-thirds of patients. Although some methodologic issues (eg, in some patients only one blood culture or one venipuncture was obtained instead of two), this study nonetheless highlights the importance of taking blood cultures prior to antimicrobial administration. Importantly, both the collection of cultures and the initiation of antimicrobial therapy should be prompt in those with the signs of severe sepsis.



REF. UpToDate 2020.03.14
Ann Intern Med. 2019 Sep 17. doi: 10.7326/M19-1696.
'감염내과 > 패혈증' 카테고리의 다른 글
| '더 많은 수액 공급'과 비교하여 '제한적 수액'은 refractory sepsis 90일째 사망률에 영향을 주지 않는다. 2023.02 (0) | 2023.02.22 |
|---|---|
| MAP target for older adults with septic shock (0) | 2020.03.15 |
| Catheter-related bloodstream infection(CRBSI) 치료에서 카테터를 제거해야 하는 경우(가능하다면 제거하는것이 원칙이지만) (0) | 2019.10.19 |
| Enterobacteriaceae로 인한 균혈증에서 항생제 사용 기간 (0) | 2019.02.10 |



