Aortic valve surgery (주로 aortic valve replacement)는 symptomatic severe AR과 일부 asymptomatic AR 환자의 주된 치료입니다. Moderate 또는 severe AR 환자들에서 aortic valve surgery의 적응증이 되는지 주기적 추적관찰을 해야 합니다. Chronic AR의 aortic valve surgery에 대한 다음 권고사항은 2014 American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology (AHA/ACC) valve guidelines Chronic AR의 aortic valve surgery에서 채택한 것입니다.
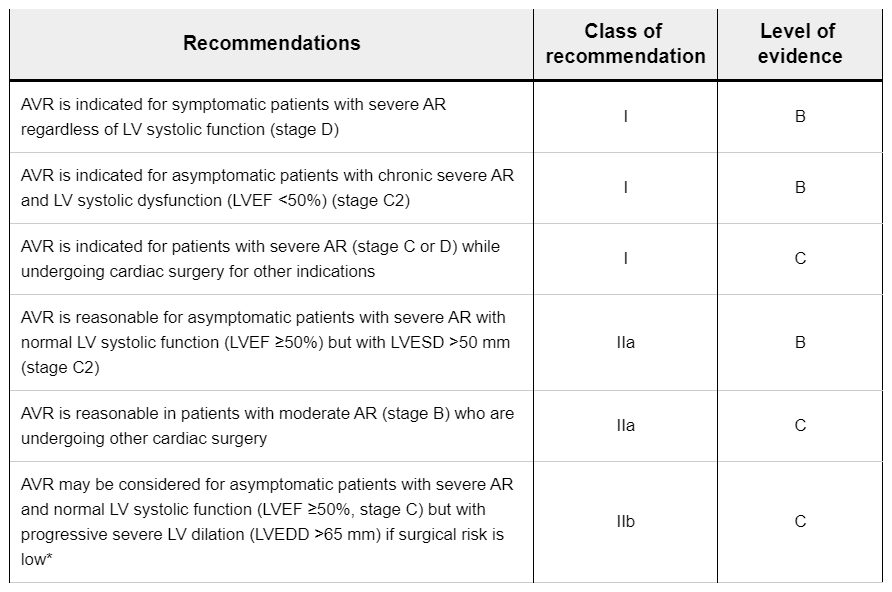
증상이 있는 severe AR (권고) I
증상이 없는 chronic severe AR의 경우에는 LVEF < 50 % (권고) I
Severe AR (stage C 또는 D)이고 다른 이유로 심장 수술을 하는 경우 (권고) I
Moderate AR (stage B)이고 다른 이유로 심장 수술을 하는 경우 (제안) IIa
증상이 없는 chronic severe AR, LVEF > 50 %의 경우에는 LVESD > 50 mm (제안) IIa
증상이 없는 chronic severe AR, LVEF > 50 %의 경우에는 LVEDD > 65 mm (제안) IIb
● Aortic valve surgery is recommended for symptomatic patients with severe AR (stage D), regardless of LV systolic function.
● Aortic valve surgery is recommended for asymptomatic patients with chronic severe AR and evidence of LV systolic dysfunction with an EF <50 percent (stage C2).
● Aortic valve surgery is suggested for asymptomatic patients with chronic severe AR with a normal LVEF (≥ 50 percent) but with an end-systolic dimension >50 mm (stage C2).
● Aortic valve surgery is suggested for asymptomatic patients with severe AR and normal LVEF (≥ 50 percent, stage C) but with progressive severe LV dilation (LVEDD > 65 mm), if surgical risk is low.
●Aortic valve surgery is recommended for patients with severe AR (stage C or D) while undergoing cardiac surgery for other indications.IIa
●Aortic valve surgery is suggested in patients with moderate AR (stage B) who are undergoing other cardiac surgery.
Summary of recommendations for aortic regurgitation intervention
Indications for AVR for chronic AR

For the strength of recommendations: Class I means the procedure/treatment should be performed/administered. Class IIa means it is reasonable to perform the procedure/administer treatment. Class IIb means the procedure/treatment may be considered. Class III means that procedure or treatment is not useful/effective and may be harmful.
For the level of evidence: Level A means multiple populations evaluated; data derived from multiple randomized clinical trials or meta-analyses. Level B means limited populations evaluated; data derived from a single randomized trial or nonrandomized studies. Level C means very limited populations evaluated; only consensus opinion of experts, case studies, or standard of care.
AR: aortic regurgitation; AVR: aortic valve replacement (valve repair may be appropriate in selected patients); ERO: effective regurgitant orifice; LV: left ventricular; LVEDD: left ventricular end-diastolic dimension; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LVESD: left ventricular end-systolic dimension; RF: regurgitant fraction; RVol: regurgitant volume.
Stages of chronic aortic regurgitation in adults
|
Stage |
Definition |
Valve anatomy |
Valve hemodynamics |
Hemodynamic consequences |
Symptoms |
|
A |
At risk of AR |
Bicuspid aortic valve (or other congenital valve anomaly) Aortic valve sclerosis Diseases of the aortic sinuses or ascending aorta History of rheumatic fever or known rheumatic heart disease IE |
AR severity: None or trace |
None |
None |
|
B |
Progressive AR |
Mild-to-moderate calcification of a trileaflet valve bicuspid aortic valve (or other congenital valve anomaly) Dilated aortic sinuses Rheumatic valve changes Previous IE |
Mild AR: Jet width <25% of LVOT; Vena contracta <0.3 cm; RVol <30 mL/beat; RF <30%; ERO <0.10 cm2; Angiography grade 1+ Moderate AR: Jet width 25 to 64% of LVOT; Vena contracta 0.3 to 0.6 cm; RVol 30 to 59 mL/beat; RF 30 to 49%; ERO 0.10 to 0.29 cm2; Angiography grade 2+ |
Normal LV systolic function Normal LV volume or mild LV dilation |
None |
|
C |
Asymptomatic severe AR |
Calcific aortic valve disease Bicuspid valve (or other congenital abnormality) Dilated aortic sinuses or ascending aorta Rheumatic valve changes IE with abnormal leaflet closure or perforation |
Severe AR: Jet width ≥65% of LVOT; Vena contracta >0.6 cm; Holodiastolic flow reversal in the proximal abdominal aorta RVol ≥60 mL/beat; RF ≥50%; ERO ≥0.3 cm2; Angiography grade 3+ to 4+; In addition, diagnosis of chronic severe AR requires evidence of LV dilation |
C1: Normal LVEF (≥50%) and LVESD ≤50 mm C2: Abnormal LV systolic function with depressed LVEF (<50%) or LVESD >50 mm or indexed LVESD >25 mm/m2 |
None; exercise testing is reasonable to confirm symptom status |
|
D |
Symptomatic severe AR |
Calcific valve disease Bicuspid valve (or other congenital abnormality) Dilated aortic sinuses or ascending aorta Rheumatic valve changes Previous IE with abnormal leaflet closure or perforation |
Severe AR: Doppler jet width ≥65% of LVOT; Vena contracta >0.6 cm; Holodiastolic flow reversal in the proximal abdominal aorta; RVol ≥60 mL/beat; RF ≥50%; ERO ≥0.3 cm2; Angiography grade 3+ to 4+; In addition, diagnosis of chronic severe AR requires evidence of LV dilation |
Symptomatic severe AR may occur with normal systolic function (LVEF ≥50%), mild-to-moderate LV dysfunction (LVEF 40 to 50%), or severe LV dysfunction (LVEF <40%) Moderate-to-severe LV dilation is present |
Exertional dyspnea or angina or more severe HF symptoms |
%: percent; AR: aortic regurgitation; ERO: effective regurgitant orifice; HF: heart failure; IE: infective endocarditis; LV: left ventricular; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LVESD: left ventricular end-systolic dimension; LVOT: left ventricular outflow tract; RF: regurgitant fraction; RVol: regurgitant volume.
REF. UpToDate 2020.03.10


