저나트륨혈증 증상 (경련, 대화 불능, 혼수)은 혈청 나트륨이 48시간 이내에 120 mEq/L 이하로 감소하여 치명적 뇌부종을 초래한 환자에서 발생할 가능성이 가장 높습니다.
|
㉮ 중증의 저나트륨혈증 증상이 있는 환자와 ㉯ 저나트륨혈증으로 인한 경미한 뇌부종조차도 견딜 수 없는 기저 뇌질환이 있는 환자에서는 비가역적 신경학적 손상을 막기 위해 혈청 나트륨은 초기에 빨리 상승시켜야 합니다. 폭넓은 임상 경험에 근거할 때 혈청 나트륨을 상승시키고 중증 증상이 있는 저나트륨혈증 환자에서 신경학적 증상을 개선시키는 유일한 빠른 방법은 hypertonic saline 주입입니다. |
한 방법은 3 % saline 100 mL를 IV bolus로 주사합니다. 이것은 혈청 나트륨을 남자에서 약 1.5 mEq/L, 여자에서는 2 mEq/L 상승시키고 뇌로부터 수분을 당겨 뇌부종의 정도를 줄입니다. 만일 신경학적 징후가 악화되거나 지속되면 10분 간격으로 1-2번 더 반복할 수 있습니다. 이와 같은 접근의 근거는 증상이 있는 저나트륨혈증 환자에서 혈청 나트륨의 4-6 mEq/L 빠른 증가는 경련과 같은 중증 증상들을 역전시킬 수 있다는 것입니다.
|
Hypertonic saline 치료의 잠재적 합병증은 저나트륨혈증을 과도하게 빠르게 교정하는 것입니다. 보통 목표 (바람직한 상승률)는 하루에 혈청 나트륨을 4-6 mEq/L/day 상승시키는 것이며, 한계 (초과해서는 안되는 상승률)는 8 mEq/L/day입니다. |
만일 교정 한계(초과해서는 안되는 상승률 : 8 mEq/L/day)를 초과했다면?

다음과 같은 특징들을 보이는 환자에서는 혈청 나트륨을 다시 낮출 것을 제안합니다.

Rescue strategy
|
㉠ chronic hyponatremia (or hyponatremia of unknown duration) ㉡ a presenting serum sodium concentration of 120 mEq/L or less ㉢ the rate of correction having exceeded the recommended limit (8 mEq/L in any 24-hour period), particularly if the patient has risk factors that make him or her unusually susceptible to ODS (serum sodium of ≤105 mEq/L, alcoholism, liver disease, malnutrition, hypokalemia |
ODS 발생 위험이 더 낮은 환자에서는 혈청 나트륨을 다시 낮추는 것은 10 - 12 mEq/L/day를 초과하는 교정률을 보인 환자로 유보되기도 합니다. 그러나 나트륨을 다시 낮추지 않는다면 48시간 동안 16 mEq/L를 초과하지 않도록 하는 것이 중요합니다.
|
Relowering of the serum sodium can reverse the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier that occurs with overly rapid correction and can prevent the infiltration of microglia that is a feature of osmotic demyelination. Relowering after overly rapid correction in rats is much more effective in preventing brain damage than the administration of glucocorticoids. |
혈청 나트륨을 다시 낮추는 방법은 D5W와 desmopressin입니다.
|
D5W, 6 mL/kg lean body weight, infused over two hours. This quantity of D5W should lower the serum sodium by approximately 2 mEq/L, and the infusion should be repeated until the therapeutic goal, |
||
|
Desmopressin, 2 mcg intravenously or subcutaneously every six hours; the dose can be increased to 4 mcg in rare patients who do not respond to lower doses. The desmopressin is continued, even after D5W infusions have ceased, to prevent the serum sodium from rising again due to the excretion of dilute urine. |
다시 나트륨을 낮출 때의 목표는 다음과 같습니다.
|
The serum should be lowered at an average rate of approximately 1 mEq/L per hour. The goal serum sodium is one that represents a rate of correction of less than 8 mEq/L in any 24-hour period and less than 16 mEq/L in any 48-hour period. Assume, for example, an alcoholic patient with an initial serum sodium of 115 mEq/L is corrected to a serum sodium of 127 mEq/L in a period of 16 hours (overly rapid correction). Desmopressin and D5W should be given to lower the sodium to less than 123 mEq/L within the next eight hours, so that the net rate of correction over the 24-hour period is less than 8 mEq/L. |
Delayed appearance of osmotic demyelination and relowering of the serum sodium
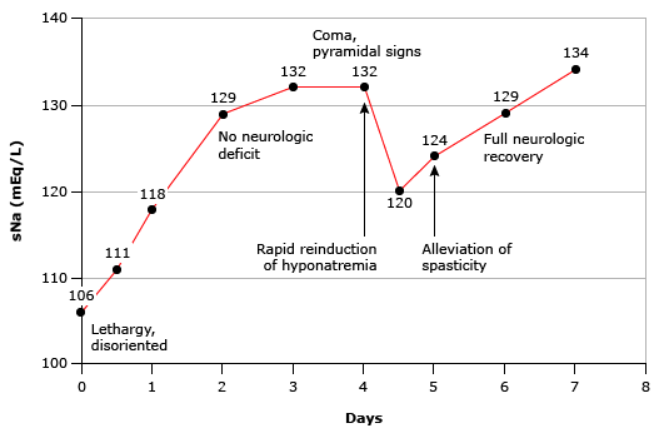
Neurologic symptoms of osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS) typically occur 2 to 6 days after correction of the hyponatremia. In this patient, severe hyponatremia was corrected too quickly (23 mEq/L in 48 hours), and coma developed 2 days later. The serum sodium was quickly relowered and then slowly corrected. Neurologic symptoms improved, which may have been due to relowering of the serum sodium or may have represented spontaneous resolution. Reproduced with permission from: Oya S, Tsutsumi K, Ueki K, Kirino T. Reinduction of hyponatremia to treat central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology 2001; 57:1931
Ref. UpToDate 2020.08.05
Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 14th edition



