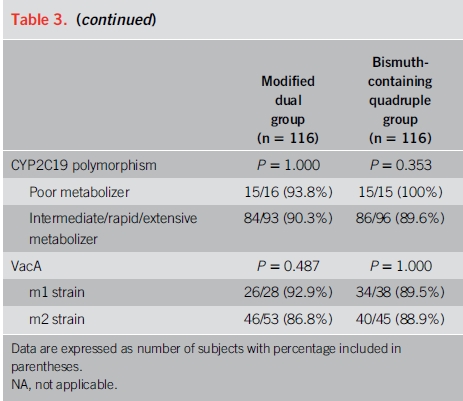
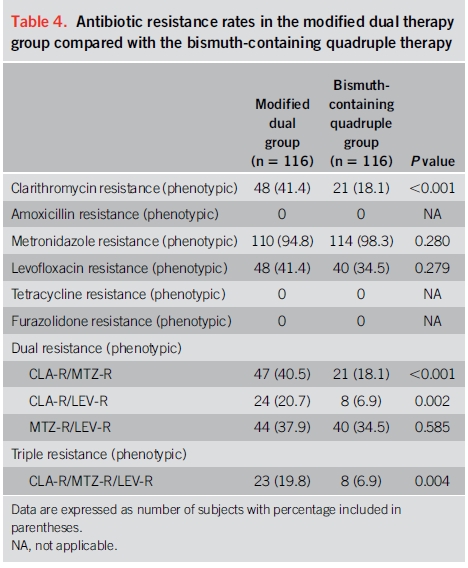
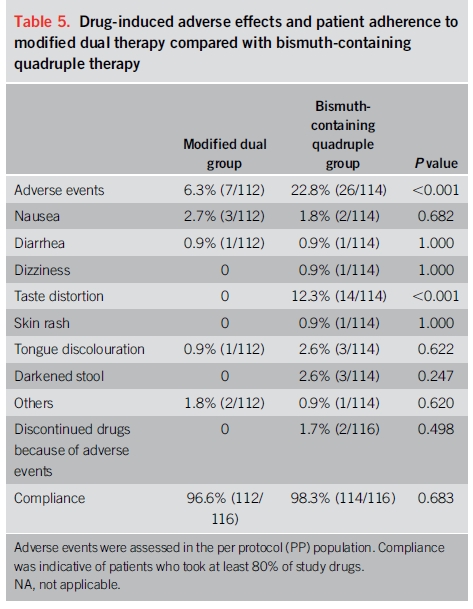
약 20% 환자는 헬리코박터 파일로리 제균(H. pylori eradication) 초기 치료에 실패합니다. 이와 같은 환자들은 salvage therapy를 필요로 합니다. 초기 항생제 치료에 실패한 환자에서의 slavage regimens은 아래 표와 테이블과 같습니다. 이 중에서 언급되는 high dose dual therapy는 amoxicillin과 PPI를 14일 동안 투약하는 것으로서 특히 dual metronidazole/clarithromycin 내성 또는 levofloxacin 내성이 의심되는 환자의 치료 방법 중 하나입니다. 유럽과 아시아에서 실시된 3 건의 무작위 임상 시험에서 salvage regime으로서 아목시실린과 PPI를 고용량 요법으로 사용한 요법의 pooled eradication rate는 78 %였습니다.
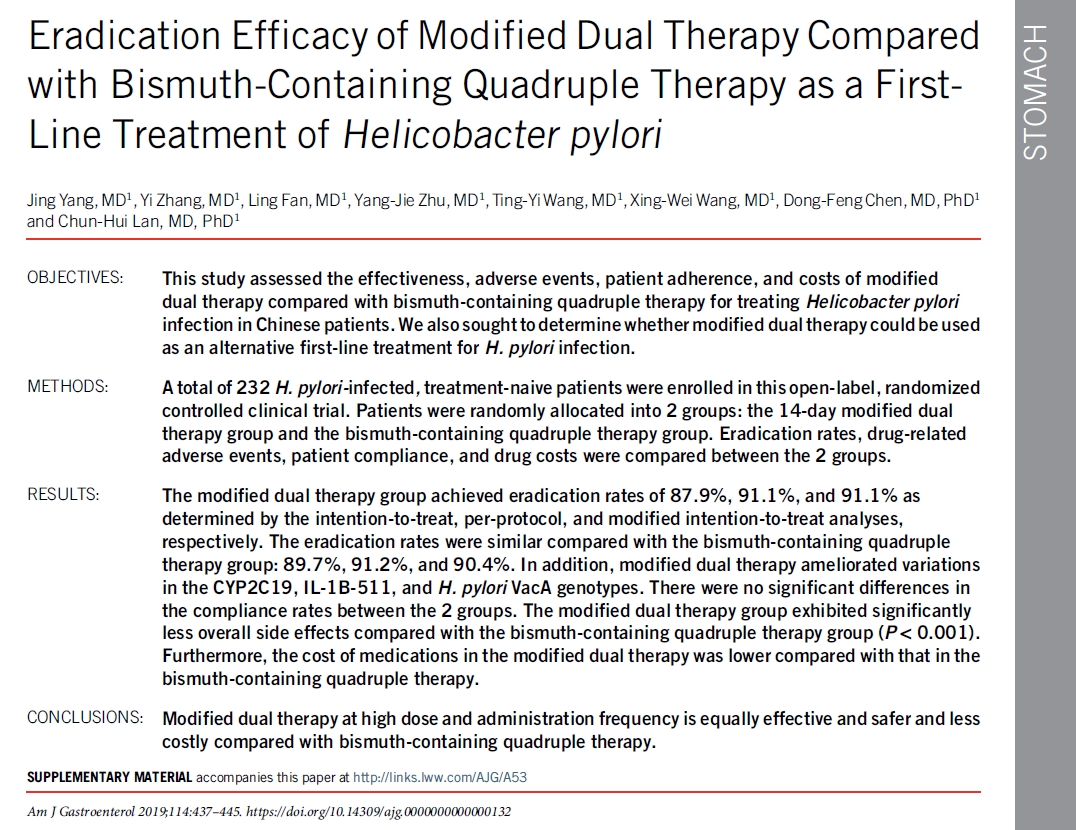
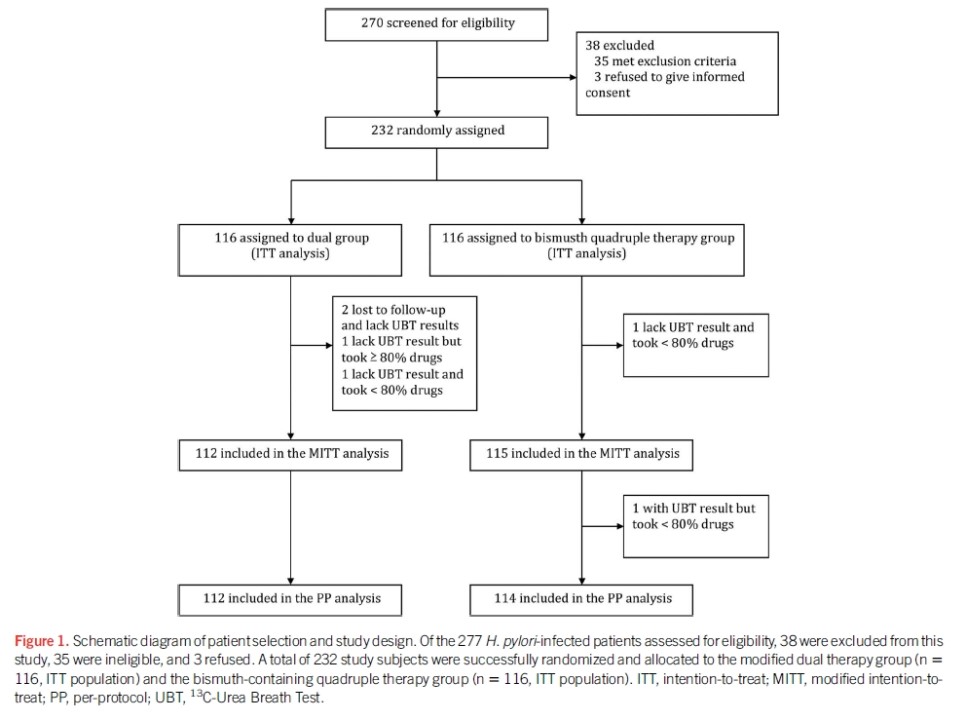
이 요법의 효능을 평가하는 연구들이 상충되었기 때문에 1 차 요법으로 high dose dual therapy의 역할은 불분명합니다. 미국과 우리나라에서 실시된 연구에서 naive 환자들에서의 박멸률은 낮았습니다(각각 72 %와 79 %). 그러나 high dose dual therapy 또는 bismuth quadruple therapy를 할당하였던 232 명의 treatment-naive 환자에서 두 집단간에 근본적인 차이는 없었습니다. High dose dual therapy는 bismuth quadruple therapy와 비교하여 치료와 관련된 부작용이 적었지만, open-label study design으로 인해 보고된 편향성이 있었을 수 있습니다.
정리)
1. Amoxicillin과 PPI를 함께 고용량 사용하는 것은 salvage regimen 중의 하나이지만 1차 약제로서의 역할은 불분명합니다.
↓
2. 중국에서 시행된 최근 무작위 연구에서 bismuth quadruple 치료와 비교하였을 때 치료율은 비슷하였습니다.
↓
3. 부작용도 더 적었으나 open label design이 이와 같은 소견에 bios를 주었을 수도 있습니다.
↓
4. 이 결과들의 타당성 입증을 위해서는 추가적인 시험들이 필요합니다.
Approach to antibiotic treatment in patients with persistent Helicobacter pylori infection
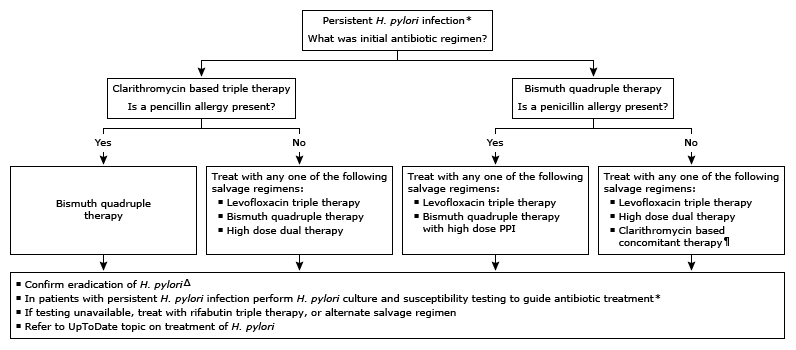
Clarithromycin based triple therapy consists of clarithromycin, amoxicillin/metronidazole, and a PPI.
Bismuth quadruple therapy consists of bismuth subsalicylate or bismuth subcitrate, metronidazole, tetracycline, and a PPI.
Levofloxacin triple therapy consists of levofloxacin, amoxicillin/metronidazole, and a PPI.
High dose dual therapy consists of amoxicillin and a PPI.
Rifabutin triple therapy consists of rifabutin, amoxicillin, and a PPI.
Clarithromycin based concomitant therapy consists of clarithromycin, amoxicillin, nitroimidazole (eg, metronidazole), and a PPI.
* Eradication of H. pylori after antibiotic treatment may be confirmed by a urea breath test, stool atigen test, or upper endoscopy-based testing. A positive result on one of these tests is indicative of a persistent H. pylori infection.
¶ Only in patients with no risk factors for macrolide resistance (no prior marolide exposure and local clarithromycin resistance known to be <15%). This regimen should be avoided if local clarithromycin resistance is unknown.
Δ Eradication of H. pylori infection can be confirmed with a urea breath test, stool antigen testing, or upper endoscopy-based testing. The choice of test depends on the need for an upper endoscopy (eg, follow-up of bleeding peptic ulcer) and local availability. H. pyloriserology should not be used to confirm eradication of H. pylori. Refer to UpToDate topic on diagnostic tests for H. pylori.
Salvage therapies for H. pylori infection
|
Regimen |
Drugs (doses)* |
Dosing frequency |
Duration (days) |
FDA approval |
|
Bismuth quadruple |
PPI (standard dose¶) |
Twice daily |
14 |
NoΔ |
|
Bismuth subcitrate (120 to 300 mg [not available in US] or 420 mg [available in North America and elsewhere as part of Pylera combination pill])[1] or Bismuth subsalicylate (300 or 524 mg)[1] |
Four times daily |
|||
|
Tetracycline (500 mg) |
Four times daily |
|||
|
Metronidazole (250 to 500 mg) |
Three to four times daily |
|||
|
Levofloxacin triple |
PPI (standard dose¶) |
Twice daily |
14 |
No |
|
Levofloxacin (500 mg) |
Once daily |
|||
|
Amoxicillin (1 gram) |
Twice daily |
|||
|
Concomitant |
PPI (standard dose¶) |
Twice daily |
10 to 14 |
No |
|
Clarithromycin (500 mg) |
Twice daily |
|||
|
Amoxicillin (1 gram) |
Twice daily |
|||
|
Metronidazole or tinidazole (500 mg) |
Two or three times daily |
|||
|
Rifabutin triple◊ |
PPI (standard dose¶) |
Twice daily |
10 |
No |
|
Rifabutin (300 mg) |
Once daily |
|||
|
Amoxicillin (1 gram) |
Twice daily |
|||
|
High-dose dual |
PPI (standard to double dose¶) |
Three to four times daily |
14 |
No |
|
Amoxicillin (1 gram three times daily or 750 mg four times daily) |
Three to four times daily |
FDA: United States Food and Drug Administration; PPI: proton pump inhibitor.
* Doses are for adults with normal renal function. Dose adjustment is warranted in patients with renal impairment for certain antibiotics (eg, levofloxacin, rifabutin, clarithromycin if end-stage disease).
¶ Standard dosing of orally administered proton pump inhibitors include: Lansoprazole 30 mg twice daily, omeprazole 20 mg twice daily, pantoprazole 40 mg twice daily, rabeprazole 20 mg twice daily, or esomeprazole 20 mg twice daily or 40 mg once daily.
Δ PPI, bismuth, tetracycline, and metronidazole prescribed separately is not an FDA-approved treatment regimen. However, Pylera, a combination product containing bismuth subcitrate, tetracycline, and metronidazole combined with a PPI for 10 days is an FDA-approved treatment regimen.
◊ Rifabutin-containing regimens should be reserved for patients with ≥3 previous eradication failures.
Reference:
Fallone CA, Chiba N, van Zanten SV, et al. The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastro 2016; 151:51.
Adapted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: American Journal of Gastroenterology. Chey WD, Leontiadis GI, Howden CW, Moss SF. ACG Clinical Guideline: Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Am J Gastroenterol 2017; 112:212. Copyright © 2017. www.nature.com/ajg.