갑상선기능저하증 위험이 있거나 임신 중인 여성에서 갑상선호르몬 처방

갑상선기능저하증 위험이 있거나 임신 중인 여성에서 갑상선호르몬 처방*
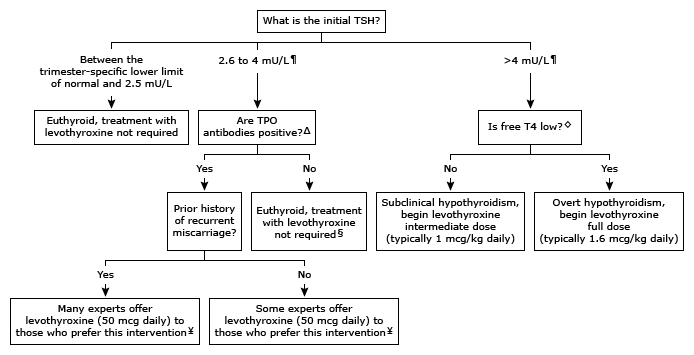
REF. UpToDate 2022.05.23
Refer to UpToDate content on screening for thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy for identification of risk factors for hypothyroidism.
TSH: thyroid-stimulating hormone; TPO: thyroid peroxidase antibodies; T4: thyroxine.
* This algorithm is intended for use in pregnant women who are not currently taking thyroid hormone.
¶ 4 mU/L or population and trimester-specific upper limit of normal, if available.
Δ The presence of TPO antibodies guides management during pregnancy. It informs the extent of autoimmunity, the risk of pregnancy loss, and the risk of postpartum thyroid dysfunction.
◊ Free T4 should be interpreted using assay method and trimester-specific reference ranges.
§ For individuals at high risk for developing hypothyroidism (eg, radioiodine treatment, hemithyroidectomy, exposure to high-dose irradiation of the head and neck), monitor TSH at least once more during the first trimester and again mid-pregnancy. Treat with levothyroxine if TSH rises above 4 mU/L.
¥ Suggestion is based upon weak evidence. The approach to management varies. If a decision is made not to treat, measure TSH approximately every 4 weeks during the first trimester, then once in each of the second and third trimesters to monitor for the development of hypothyroidism. Treat with levothyroxine if TSH rises above 4 mU/L.
